[Codegate 2020 Final write-up] Matrixvm-Rev
원래 블로그 글은 영어 공부를 위해서 영어로 쓰려고 계획했는데 쓰다보니 생각보다 시간이 많이 걸린다. 그래서 일단 첫번째 글은 한글로 적어보려고 한다. 아마 이 글 이후에는 작성할 때의 멘탈에 따라서 영어, 한국어를 번갈아가면서 퍼블리시 할 것 같다.
그동안 개인 프로젝트와 회사일을 핑계로 CTF 대회를 참가하지 않은지 약 2년이 넘었는데 그동안 대회의 문제 트렌드가 너무 많이 바뀌었다.
물론 이전에 회사에 다닐때 같이 일하던 동료가 주말마다 CTF를 나가며 어떤 문제가 나오는지 간단하게 브리핑(?)을 해줘서 대충 알고 있었지만 실제로 접해본건 처음이라..
다른 팀에 비해서 문제를 푸는 속도도 느려지고 그동안 리버싱을 많이 안해서인지 코드를 분석하는 속도와 능력이 감소한것 같아 이대론 안되겠다 싶어 대회가 끝난 뒤에 시간이 날때마다 틈틈히 리버싱 문제들을 주르륵 풀어보고 있다.
MatrixVM
이름에서 볼 수 있듯이 행렬 VM 이라고 하는 문제이다. 실제로 이 문제를 풀때 CPU 바이너리와 가상화된 코드를 분석하는 시간보다 선형대수학에 대해 공부하는 시간이 좀 더 길었다.
학생 시절(놀랍게도 아직 대학생이다)에 수학과 담을 쌓고 살아왔던 나는 코드를 분석하는 것 보다 행렬을 지지고 볶는것을 보는게 더 큰 위기였다.
다행히도 수학을 잘 하는 친구와 같이 대회를 나갔던 멤버들의 도움을 받아 풀 수 있었다…
문제는 2가지 바이너리가 주어졌다.
- matrixvm : 가상화 코드를 실행해주는 바이너리
- prob.mv : 가상화 코드가 담겨있는 코드
사실.. 이번이 가상화 문제를 처음 접했던 대회라서 어떻게 풀어야 할지 생각을 해보다가 아래와 같은 순서로 풀기로 했다.
- matrixvm 을 분석해서 명령어 셋을 분석한다
- prob.mv 를 해석할 수 있는 스크립트를 제작한다
- 2를 돌려서 나온 결과를 분석해서 로직을 알아낸다.
- 선형대수학을 친구들에게 물어본다.
- 3, 4를 이용해서 어떻게 flag를 얻어낼지 고민한다.
Analyising a binary
Binary 실행 순서
크게 이 바이너리를 분석하면 아래와 같이 동작한다
- argv[1] 로 들어온 가상화된 코드 파일을 연다.
- 코드들을 파싱해서 각자 구조체를 만들어서 명령어들을 순서대로 Double Linked List 형태 연결시킨다.
- 명령어는 0x0 ~ 0x5까지 존재하며 2에서 파싱한 명령어를 순차적으로 실행한다.
Parsing an opcode
파일을 로드하고 위 과정 중 2 과정에서 명령어 별로 파싱을 진행한다.

(일부 변환해놓은 hex-ray 정보가 잘못되어 있을 수 있는데 수정하기가 귀찮아서 패스했습니다)
- 0x0 : opcode (1 byte) + coordinate_x (8 bytes) + coordinate_y (8 bytes) + matrix_data (8 * x * y)
- 각 요소는 8byte 씩 차지함.
- 0x1 ~ 0x3 : opcode (1byte) + data (16 bytes)
- 0x4 : opcode (1byte) + data (48 bytes)
- 0x5 : opcode (1byte) + data (16 bytes)
data에는 x, y 의 좌표값 또는 matrix의 id 넘버(matrix 를 구분하기 위한 용도) 등이 들어간다.
일단 이 정보 만으로 parser를 제작할 수 있지만 좀더 opcode 별로 대충 어떤걸 하는지 알아보기 위해서 opcode 별 역할을 간단하게 조사하기로 했다.
Opcode 별 역할

이때 명령어별로 역할은 다음과 같다
- 0x0 : 새로운 matrix 생성
- 0x1 : matrix의 곱 연산 (numpy 의 .dot() 함수와 같은 역할)
- 0x2 : User 의 input 을 받고 matrix에 저장한다. (getchar() 함수)
- 0x3 : matrix의 데이터를 출력한다. (putchar함수)
- 0x4 : matrix의 데이터를 이동시킨다. (Assembly의 mov 명령어)
- 0x5 : 만약 matrix의 결과가 0이 아니라면 Offset 만큼 명령어를 건너뛴다. (flag 검증 루틴)
Writing a parser
위 정보들을 토대로 간단한 파서를 제작했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
from pwn import *
f = open("prob.mv", "rb")
code = f.read()
f.close()
idx = 0
while True:
print("*"*100)
if (len(code) == idx):
break
opcode = code[idx]
print("opcode : ", opcode)
idx += 1
if opcode == 0x0:
print("[ALLOCATE] Allocate new matrix")
print(hexdump(code[idx:idx+24]))
id = u64(code[idx:idx+8])
x = u64(code[idx+8:idx+16])
y = u64(code[idx+16:idx+24])
print("id, x, y : ", hex(id), x,y)
idx += 24
print(hexdump(code[idx:idx+(8*x*y)]))
idx += 8*x*y
elif opcode >= 1 and opcode <= 3:
if opcode == 1:
print("[MUL]")
elif opcode == 2:
print("[READ]")
elif opcode == 3:
print("[PRINT]")
print("copy data into new malloc")
print(hexdump(code[idx:idx+24]))
idx += 24
elif opcode == 4:
print("[MOVE DATA]")
dst_id = u64(code[idx:idx+8])
dst_x = u64(code[idx+8:idx+16])
dst_y = u64(code[idx+16:idx+24])
src_id = u64(code[idx+24:idx+32])
src_x = u64(code[idx+32:idx+40])
src_y = u64(code[idx+40:idx+48])
print("dst", hex(dst_id), dst_x, dst_y, "src", hex(src_id), src_x, src_y)
print(hexdump(code[idx:idx+48]))
idx += 48
elif opcode == 5:
print("COMPARE")
print("copy data into new malloc")
print(hexdump(code[idx:idx+16]))
idx += 16
else:
print("unknown opcode", opcode)
print(hexdump(code[idx:idx+32]))
print(opcode)
break
블로그용으로 정리한 코드가 아니라서 정말 깔끔하지 않다. (심지어 맨정신으로 짠 코드도 아니라..)
아무튼 이러한 코드를 돌리면 아래 사진 처럼 결과가 나온다.
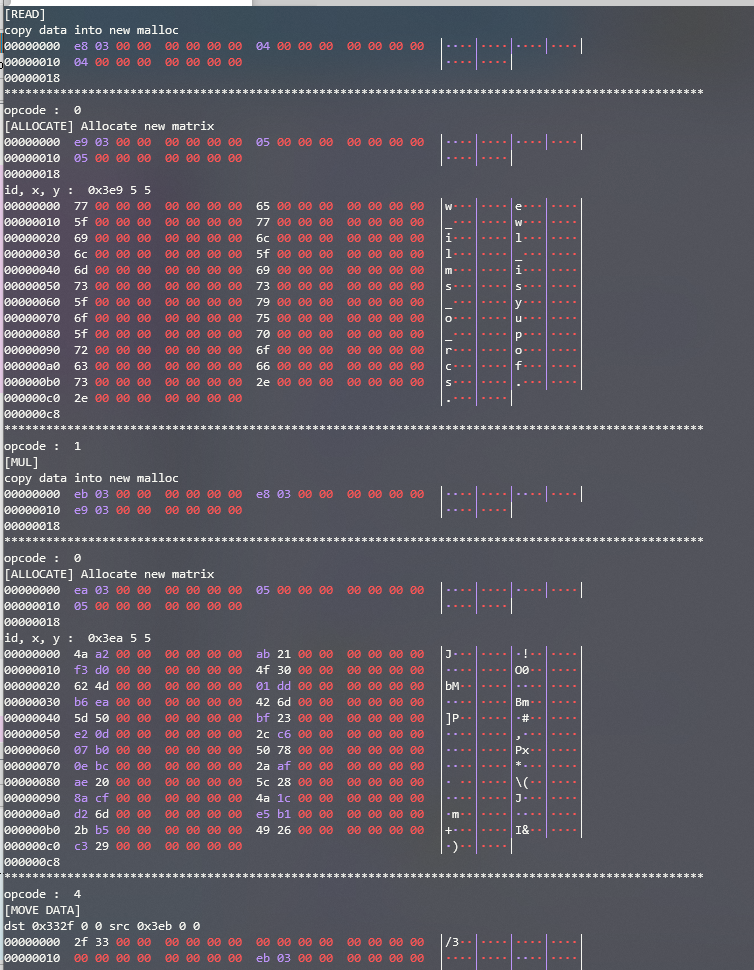
중간중간 we_will_miss_you_procfs.. 라는 글자고 보이고 이상한 데이터도 막 보인다.
이를 보면서 대충 어떻게 굴러가는 코드인지 파악하고 유저의 입력, 연산하는 순서를 파악했다.
그리고 위 코드를 약간 변형해서 좀더 알아보기 수월하게 가상화된 코드를 수도코드로 변환하는 작업을 진행했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
from pwn import *
import numpy as np
import string
import json
f = open("prob.mv", "rb")
code = f.read()
f.close()
mdict = {}
user_input_str = ""
user_input_str += "\x00"*(25-len(user_input_str))
user_input = [ord(c) for c in user_input_str]
user_input_tmp = {}
user_input_tmp["x"] = 5
user_input_tmp["y"] = 5
user_input_tmp["matrix"] = np.reshape(user_input, (5, 5))
mdict[0x3e8] = user_input_tmp
idx = 0
while True:
if (len(code) == idx):
# If code ended
break
opcode = code[idx]
idx += 1
if opcode == 0x0:
tmp = {}
id = u64(code[idx:idx+8], sign="signed")
x = u64(code[idx+8:idx+16], sign="signed")
y = u64(code[idx+16:idx+24], sign="signed")
tmp["x"] = x
tmp["y"] = y
idx += 24
tmpcode = code[idx:idx+(8*x*y)]
tmp["code"] = []
matrix = [[0 for w in range(x)] for h in range(y)]
for z in range(0, len(tmpcode), 8):
v = u64(tmpcode[z:z+8], sign="signed")
tmp["code"].append(v)
idx += 8*x*y
result = (np.reshape(tmp["code"], (x, y)))
tmp["matrix"] = result
if id == 0x3e8:
# 0x3e8 has already declared. (user_input_str)
print(("mdict[%x]=" %id), mdict[id]["matrix"])
continue
mdict[id] = tmp
print(("mdict[%x]=" %id), mdict[id]["matrix"])
elif opcode >= 1 and opcode <= 3:
if opcode == 1:
result = u64(code[idx:idx+8], sign="signed")
m1 = u64(code[idx+8:idx+16], sign="signed")
m2 = u64(code[idx+16:idx+24], sign="signed")
m1m = mdict[m1]["matrix"]
m2m = mdict[m2]["matrix"]
new_matrix = m1m.dot(m2m)
tmp = {}
tmp["x"] = new_matrix.shape[0]
tmp["y"] =new_matrix.shape[1]
tmp["matrix"] = new_matrix
mdict[result] = tmp
print("mdict[%x] = mdict[%x].dot((mdict[%x]))" % (result, m1, m2))
idx += 24
elif opcode == 4:
dst_id = u64(code[idx:idx+8], sign="signed")
dst_x = u64(code[idx+8:idx+16], sign="signed")
dst_y = u64(code[idx+16:idx+24], sign="signed")
src_id = u64(code[idx+24:idx+32], sign="signed")
src_x = u64(code[idx+32:idx+40], sign="signed")
src_y = u64(code[idx+40:idx+48], sign="signed")
mdict[dst_id]["matrix"][dst_x][dst_y] = mdict[src_id]["matrix"][src_x][src_y]
tmpstr = 0
if src_id == 0x3ec:
tmpstr = (mdict[src_id]["matrix"][src_x][src_y])
print('mdict[%x][%d][%d] = mdict[%x][%d][%d]'%(dst_id, dst_x, dst_y, src_id, src_x, src_y), tmpstr)
idx += 48
elif opcode == 5:
id = u64(code[idx:idx+8], sign="signed")
v = mdict[id]["matrix"][0]
print("compare : mdict[%x][0][0] == 0" % id)
print(v, v[0] == 0, mdict[id]["matrix"])
print(mdict[0x3eb]) # refer Tips section
exit(-1) # this allows to stop at first comparing operation
idx += 16
else:
print("unknown opcode", opcode)
print(hexdump(code[idx:idx+32]))
print(opcode)
break
아래는 위 코드의 실행 결과이다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
# 1. 계산을 위한 문제에 정의된 matrix 여러개 생성
mdict[332c]= [[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35
36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53
54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71
72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89
90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99]
[100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117
118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135
136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153
154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171
172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189
190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199]
[200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217
218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235
236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253
254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271
272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289
290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299]]
mdict[332d]= [[1]
[1]]
mdict[332e]= [[ 1]
[-1]]
mdict[332f]= [[0 0]]
mdict[3330]= [[0]]
# 2. 유저의 Input (25byte) 을 받고 matrix(0x3e8)에 저장시킴
mdict[3e8]= [[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]]
# 3. 2번의 matrix와 문제에 정의된 5*5 matrix(알수 없는 데이터가 담긴 행렬)을 곱함.
mdict[3e9]= [[119 101 95 119 105]
[108 108 95 109 105]
[115 115 95 121 111]
[117 95 112 114 111]
[ 99 102 115 46 46]]
mdict[3eb] = mdict[3e8].dot((mdict[3e9]))
# 4. 추가로 알수없는 데이터가 담긴 matrix을 몇개 더 생성하고 3번에서 곱한 matrix의 데이터를 또 좌표별로 가져와서 곱하는 과정을 몇번 반복.
mdict[3ea]= [[41546 8619 53491 12367 19810]
[56577 60086 27970 20573 9151]
[ 3554 50732 45063 30800 48142]
[44842 8366 10332 53130 7242]
[28114 45541 46379 9801 10691]]
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][0][0] 0
mdict[7d0] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][0][0] = mdict[7d0][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][0][1] 0
mdict[7d1] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][0][1] = mdict[7d1][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][0][2] 0
mdict[7d2] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][0][2] = mdict[7d2][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][0][3] 0
mdict[7d3] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][0][3] = mdict[7d3][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][0][4] 0
mdict[7d4] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][0][4] = mdict[7d4][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][1][0] 0
mdict[7d5] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][1][0] = mdict[7d5][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][1][1] 0
mdict[7d6] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][1][1] = mdict[7d6][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][1][2] 0
mdict[7d7] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][1][2] = mdict[7d7][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][1][3] 0
mdict[7d8] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][1][3] = mdict[7d8][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][1][4] 0
mdict[7d9] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][1][4] = mdict[7d9][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][2][0] 0
mdict[7da] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][2][0] = mdict[7da][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][2][1] 0
mdict[7db] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][2][1] = mdict[7db][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][2][2] 0
mdict[7dc] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][2][2] = mdict[7dc][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][2][3] 0
mdict[7dd] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][2][3] = mdict[7dd][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][2][4] 0
mdict[7de] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][2][4] = mdict[7de][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][3][0] 0
mdict[7df] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][3][0] = mdict[7df][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][3][1] 0
mdict[7e0] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][3][1] = mdict[7e0][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][3][2] 0
mdict[7e1] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][3][2] = mdict[7e1][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][3][3] 0
mdict[7e2] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][3][3] = mdict[7e2][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][3][4] 0
mdict[7e3] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][3][4] = mdict[7e3][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][4][0] 0
mdict[7e4] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][4][0] = mdict[7e4][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][4][1] 0
mdict[7e5] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][4][1] = mdict[7e5][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][4][2] 0
mdict[7e6] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][4][2] = mdict[7e6][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][4][3] 0
mdict[7e7] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][4][3] = mdict[7e7][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][4][4] 0
mdict[7e8] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][4][4] = mdict[7e8][0][0] 0
# 4. 추가로 알수없는 데이터가 담긴 matrix을 몇개 더 생성하고 3번에서 곱한 matrix의 데이터를 또 좌표별로 가져와서 곱하는 과정을 몇번 반복.
mdict[3ec]= [[ 66767 74378 98601 96720 115270 59426 95089 80703 115942 59188
58826 82702 108504 102446 102655 64693 89909 70993 101607 53330
102259 59728 64083 66997 103118]]
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][0] 66767
mdict[7e9] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][4][3] = mdict[7e9][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][1] 74378
mdict[7ea] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][1][3] = mdict[7ea][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][2] 98601
mdict[7eb] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][3][0] = mdict[7eb][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][3] 96720
mdict[7ec] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][2][2] = mdict[7ec][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][4] 115270
mdict[7ed] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][1][1] = mdict[7ed][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][5] 59426
mdict[7ee] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][3][2] = mdict[7ee][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][6] 95089
mdict[7ef] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][2][4] = mdict[7ef][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][7] 80703
mdict[7f0] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][2][3] = mdict[7f0][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][8] 115942
mdict[7f1] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][1][0] = mdict[7f1][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][9] 59188
mdict[7f2] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][2][0] = mdict[7f2][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][10] 58826
mdict[7f3] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][3][1] = mdict[7f3][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][11] 82702
mdict[7f4] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][1][2] = mdict[7f4][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][12] 108504
mdict[7f5] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][0][2] = mdict[7f5][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][2][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][13] 102446
mdict[7f6] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][2][1] = mdict[7f6][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][2] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][14] 102655
mdict[7f7] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][4][2] = mdict[7f7][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][15] 64693
mdict[7f8] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][0][1] = mdict[7f8][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][16] 89909
mdict[7f9] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][4][0] = mdict[7f9][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][17] 70993
mdict[7fa] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][0][4] = mdict[7fa][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][18] 101607
mdict[7fb] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][0][0] = mdict[7fb][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][19] 53330
mdict[7fc] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][3][4] = mdict[7fc][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][3][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][20] 102259
mdict[7fd] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][3][3] = mdict[7fd][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][1][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][21] 59728
mdict[7fe] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][1][4] = mdict[7fe][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][4] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][22] 64083
mdict[7ff] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][4][4] = mdict[7ff][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][3] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][23] 66997
mdict[800] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][0][3] = mdict[800][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][4][1] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][24] 103118
mdict[801] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][4][1] = mdict[801][0][0] 0
mdict[3330][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][0] 0
# 5. 4번의 결과를 한글자씩 뽑아서 결과가 0인지 확인함. (25번 반복)
compare : mdict[3330][0][0] == 0
[-60061] False [[-60061]]
참고
- .dot() 는 numpy 의
Dot product of two arrays를 수행하는 함수다. (행렬곱) - 공식문서
파싱된 명령어가 꽤 많으니 가상화된 코드의 로직을 간단하게 정리하자면 아래와 같다.
- 계산을 위한 문제에 정의된 matrix 여러개 생성
- 유저의 Input (25byte) 을 받고 5*5 matrix에 저장시킴
- 2번의 matrix와 문제에 정의된 5*5 matrix(알수 없는 데이터가 담긴 행렬)을 곱함.
- 추가로 알수없는 데이터가 담긴 5*5 matrix을 2개 더 생성하고 3번에서 곱한 matrix의 데이터를 또 좌표별로 가져와서 곱하는 과정을 몇번 반복.
- 4번의 결과를 한글자씩 뽑아서 결과가 0인지 확인함. (25번 반복)
- 만약 5번의 결과가 25번 모두 0일 경우 Correct 출력
- 만약 5번의 결과가 한번이라도 틀릴 경우 Wrong 출력
위의 과정은 너무 길어서 첫 번째 Flag 를 비교하는 로직만 뽑아서 보기로 했다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# 1. 계산을 위한 문제에 정의된 matrix 여러개 생성
mdict[332d]= [[1]
[1]]
mdict[332e]= [[ 1]
[-1]]
# 2. 유저의 Input (25byte) 을 받고 matrix(0x3e8)에 저장시킴
# userinput 은 \x00 * 25개로 설정
mdict[3e8]= [[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]
[0 0 0 0 0]]
# 3. 2번의 matrix와 문제에 정의된 5*5 matrix(알수 없는 데이터가 담긴 행렬)을 곱함.
mdict[3e9]= [[119 101 95 119 105]
[108 108 95 109 105]
[115 115 95 121 111]
[117 95 112 114 111]
[ 99 102 115 46 46]]
mdict[3eb] = mdict[3e8].dot((mdict[3e9]))
# 4. 추가로 알수없는 데이터가 담긴 matrix을 몇개 더 생성하고 3번에서 곱한 matrix의 데이터를 또 좌표별로 가져와서 곱하는 과정을 몇번 반복.
mdict[3ea]= [[41546 8619 53491 12367 19810]
[56577 60086 27970 20573 9151]
[ 3554 50732 45063 30800 48142]
[44842 8366 10332 53130 7242]
[28114 45541 46379 9801 10691]]
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ea][0][0] 0
mdict[7d0] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332d]))
mdict[3eb][0][0] = mdict[7d0][0][0] 0
# 4. 추가로 알수없는 데이터가 담긴 matrix을 몇개 더 생성하고 3번에서 곱한 matrix의 데이터를 또 좌표별로 가져와서 곱하는 과정을 몇번 반복.
mdict[3ec]= [[ 66767 74378 98601 96720 115270 59426 95089 80703 115942 59188
58826 82702 108504 102446 102655 64693 89909 70993 101607 53330
102259 59728 64083 66997 103118]]
mdict[332f][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][0] 0
mdict[332f][0][1] = mdict[3ec][0][18] 101607
mdict[7fb] = mdict[332f].dot((mdict[332e]))
mdict[3eb][0][0] = mdict[7fb][0][0] 0
# 5. 4번의 결과를 한글자씩 뽑아서 결과가 0인지 확인함. (25번 반복)
# 0번째 플래그 확인
mdict[3330][0][0] = mdict[3eb][0][0] 0
compare : mdict[3330][0][0] == 0
상세 순서로 정리하면 아래와 같다.
- user_input matrix인 3e8 과 matrix 3e9 을 행렬곱 연산하고 결과를 matrix 3eb에 저장한다
- matrix 3eb의 (0,0) 값과 matrix 3ea의 (0,0) 값 (41546)를 matrix 332f로 가져온다
- matrix 332f 와 matrix 332d 를 행렬곱 연산하고 결과를 matrix 3eb의 (0,0) 에 넣는다
- 결과적으로는 (matrix 3eb의 (0,0) 값 * 1 + 41546 * 1) 와 같다.
- matrix 3eb의 (0,0) 값과 matrix 3ec (0, 18) 값 (101607)를 matrix 332f로 가져온다.
- matrix 332f 와 matrix 332e 를 행렬곱 연산 하고 결과를 matrix 7fb 에 저장한다
- 결과적으로는 (3번의 결과 * 1 + 101607 * (-1)) 와 같다
- 이때 결과가 0이 되려면 matrix 3eb의 (0,0) 값은 101607이어야 한다
- matrix 7fb 의 (0,0)값을 matrix 3eb (0,0) 으로 가져온다
- matrix 3eb 의 (0,0)값을 matrix 3330 (0,0) 으로 가져온다
- matrix 3330의 (0,0)값이 0인지 확인한다. (0일 경우 통과)
복잡하다… 그런데 이 과정을 잘 보면 간단하게 정리가 가능하다
- 5번 연산과정을 정리하면 아래와 같다
- (matrix 3eb의 (0,0) 글자 * 1 + 41546 * 1) * 1 + 101607 * (-1) = 0
- ⇒ ((matrix 3e8 과 matrix 3e9 을 행렬곱 연산한 결과의 0, 0) * 1 + 41546 * 1) * 1 + 101607 * (-1) = 0
- ⇒ ((matrix 3e8 과 matrix 3e9 을 행렬곱 연산한 결과의 0, 0) + 41546) - 101607 = 0
- ⇒ (matrix 3e8 과 matrix 3e9 을 행렬곱 연산한 결과의 0, 0) = 60061
이렇게 간단하게 정리가 된다.
Tips
팁으로 user_input의 모든 값을 \x00 으로 세팅하고 compare 하는 연산 을 할때 0x3eb를 출력하면 위 60061 같은 연산 목표값을 구할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
[[-60061, -56074, -55013, -54630, -51183],
[-59365, -55184, -54732, -53805, -50577],
[-55634, -51714, -51657, -49903, -46947],
[-53759, -50460, -49094, -49129, -46088],
[-61795, -57577, -56276, -56966, -53392]]
결론으로는 matrix 3e8 과 matrix 3e9 의 행렬곱연산 결과가 위 행렬의 결과가 같아야한다.
How to solve
위 결론을 통해서
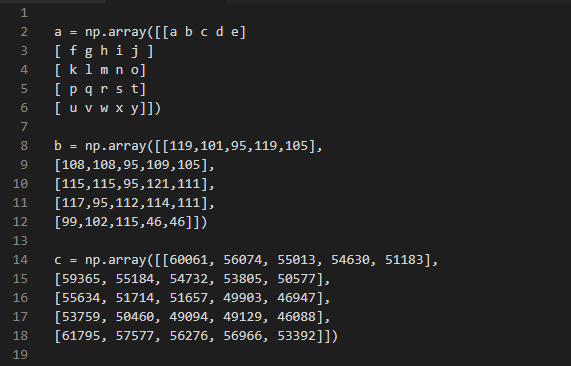
- matrix a(3e8) 와 matrix b(3e9) 의 행렬곱 연산결과가 matrix c 여야 조건이 충족된다.
- 그러므로 user input 에 따라 결정되는 matrix a를 구해야 한다.
- matrix a는 아래와 같이 구할 수 있다.
- matrix c * matrix b^{-1} = matrix a
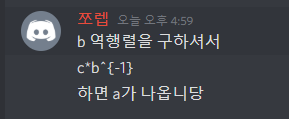
바로 계산해보자
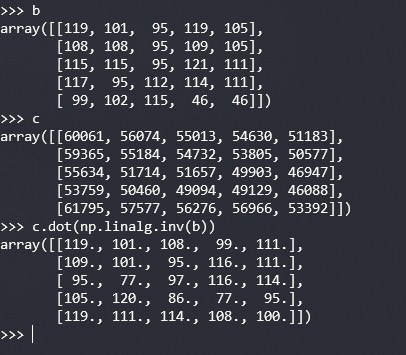
이뻐보이는 array 값들이 나왔다.
간단하게 reshape 를 통해서 1차원 배열로 변환후 문자열로 변환하면..
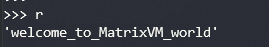
플래그가..
Flag : welcome_to_MatrixVM_world
ps. 수학공부를 열심히 하지 않은것이 후회되는 하루였다.