[Codegate 2020 Final write-up] Rabbit
They provide only one binary named rabbit. This is 32bit binary which is running on Linux.
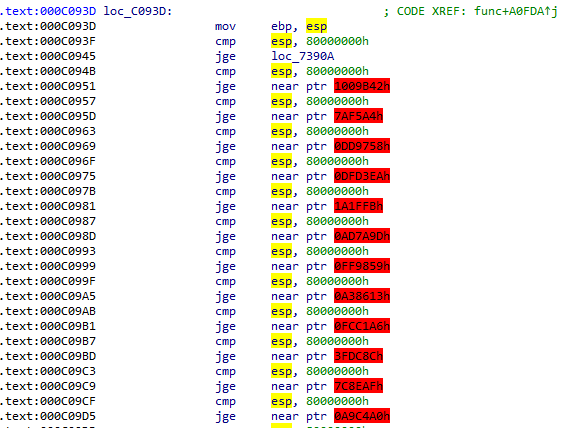
This binary is obfuscated to prevent exposing a logic. And this looks some jump opcodes were injected into original code to make it harder to follow a control flow. So I tried to understand a flow by tracing with GDB but it’s not good way to follow the whole logic. So I started to find some code patterns for writing a de-obfuscating script.
De-obfuscating the binary
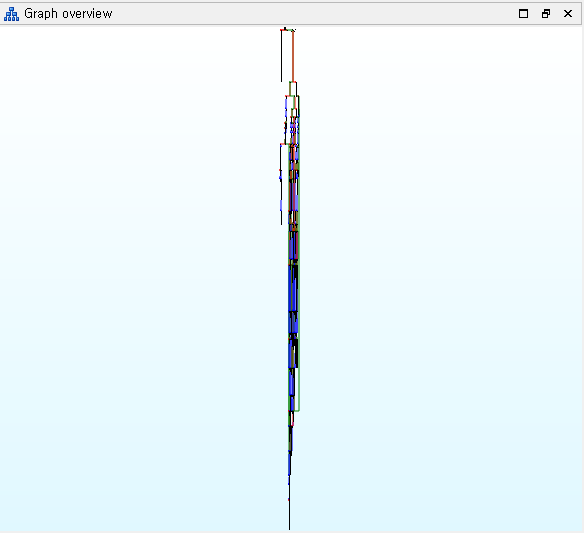
The binary is literally bursted and it’s hard to follow a control flow. So I decided to make a de-obfuscation script first.
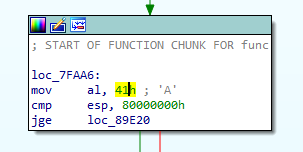
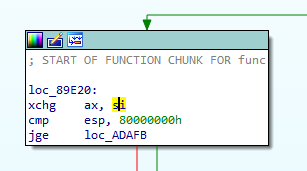
These code block has two same instructions. First one is cmp esp, 0x80000000 and the other one is cmp jge destination . And these makes new conditional statement on the graph.
The file is 32bit ELF binary. On Linux, register ESP must be higher than 0xbf?????? in most cases. So above comparisons are always TRUE. So we can change the instruction JGE to JMP Instruction to make simplify flow graph. This script helps to convert the instruction JGE to JMP instruction until the obfuscated function finished.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
from pwn import *
from capstone import *
elf = ELF('./rabbit')
# List symbols at program
target = "func" # name of obfuscated function
func = elf.symbols[target]
print(func)
basesize = func
idx =0
t2 = False
patched_jmp = []
while True:
if idx > 1000:
break
asd = elf.read(func, 20)
print(disasm(asd,basesize,3))
md = Cs(CS_ARCH_X86, CS_MODE_32)
md.detail = True
i = md.disasm(asd, func, 3)
i1 = next(i)
i2 = next(i)
i3 = next(i)
i.close()
#input(">")
if i1.mnemonic == "ret":
elf.save("./rabbit.patched")
input("> RET DETECTED and saved")
if t2:
t2 = False
if i1.mnemonic == "je":
if (i2.operands[0].imm) in patched_jmp:
print("already patched for next instruction. pass!")
#print("T2 detect / ", i2.operands[0].imm-i1.size)
func = i1.operands[0].imm
print("go to ", hex(func))
#patched_jmp.append(i2.operands[0].imm-i1.size)
continue
else:
func = func + i1.size
patched_jmp.append(i2.operands[0].imm)
continue
print(i1, i2, i3)
if i1.size == 6 and i1.mnemonic == "cmp":
print("good", i1.size, i1.operands[0], i1.operands[1].imm == 0x80000000)
print("good1", i2.operands[0], hex(i2.operands[0].imm))
elif i1.mnemonic == "test" and i2.mnemonic == "jmp":
t2 = True
#if i2.operands[0].imm in patched_jmp:
# func = func + i1.size
# print("[!] already patched... skipped this instruction")
# continue
#testsize = i1.size
#print("NEW 0x%x" % (i2.operands[0].imm))
#patched_jmp.append((i2.operands[0].imm))
#print(patched_jmp)
func = i2.operands[0].imm#-i1.size
continue
elif i1.mnemonic == "jmp":
print("Jumping to the 0x%x", i1.operands[0].imm)
func = i1.operands[0].imm
continue
else:
print("no", i1.size)
func = func + i1.size
print("="*100)
continue
size = i1.size
elf.asm(func+size, 'jmp 0x%x' % (i2.operands[0].imm))
print("patch ", 'jmp 0x%x' % (i2.operands[0].imm))
print("after")
asd = (elf.read(func, 20))
print(disasm(asd,basesize,3))
func = (i2.operands[0].imm)
idx +=1
print("="*100)
print("="*100)
print("="*100)
elf.save("./rabbit.patched")
The script is literally messy cause I am not familiar with Pwntools and cap/keystones. But It works fine :)
Analyzing the binary
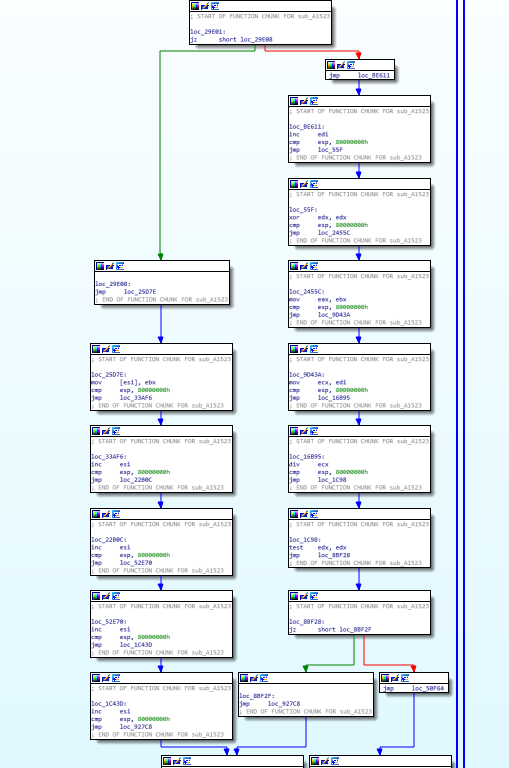
Yes! Now we removed meaningless branches and simplified a flow graph on IDA. Also now we have to understand the logic of this binary!

Hex-ray is working well and I could understand the whole logic of ‘func’ function.
As summery of this ‘func’ function
- Finding prime numbers until 0x100000, If found, store it on 0x41414000.
- After 1 finished, The binary makes another data table on 0x42424000.
After ‘func’ finished, The Main function refers table 0x42424000 to print our flag.
But there is a big problem of this function. While getting prime numbers on ‘func’ function, It takes too long time to execute large loop.
Once I searching on the internet, I found a way to calculate prime numbers until 0x100000 and this takes less time to get prime numbers.
Also I found the example code on the internet, Also I implemented logic 2 on the below code.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h> //sqrt()
#define NUM 1048576
int main(void)
{
static int prime[NUM + 1] = { 0, };
static int primefinal[NUM + 1] = { 0, };
static char finaldata[NUM * 4 + 1] = {0,};
int i, j, Limit;
for (i = 2; i <= NUM; i++)
prime[i] = 1;
Limit = (int)sqrt(NUM);
for (i = 2; i <= Limit; i++) {
if (prime[i] == 1) {
for (j = 2 * i; j <= NUM; j++) {
if (j % i == 0)
prime[j] = 0;
}
}
}
int idxz = 0;
for (i = 2; i <= NUM; i++)
if (prime[i] == 1)
primefinal[idxz++] = i;
printf("\n");
int idx2 = 0;
int idx = 0;
int wtf = 82025;
printf("Start calculating.. \n");
do {
idx2 = idx;
do {
int mapidx = primefinal[idx2] + primefinal[idx];
if (mapidx > 0x100000 * 4) {
printf("assert..%x %x %x %x %x", mapidx, primefinal[idx2], primefinal[idx], idx2, idx);
return 0;
}
//printf("%d\n", mapidx);
finaldata[mapidx]++;
1 + 1;
idx += 1;
1 + 1;
} while (idx != wtf);
idx = idx2 + 1;
} while (idx2 + 1 != wtf);
return 0;
}
Getting a flag

There is a print logic on Main function. It refers data from above table which are index of each flag characters.
So I just added printing code for getting final flag string.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h> //for using sqrt
#define NUM 1048576
int main(void)
{
static int prime[NUM + 1] = { 0, };
static int primefinal[NUM + 1] = { 0, };
static char finaldata[NUM * 4 + 1] = {0,};
int i, j, Limit;
for (i = 2; i <= NUM; i++)
prime[i] = 1;
Limit = (int)sqrt(NUM);
for (i = 2; i <= Limit; i++) {
if (prime[i] == 1) {
for (j = 2 * i; j <= NUM; j++) {
if (j % i == 0)
prime[j] = 0;
}
}
}
int idxz = 0;
for (i = 2; i <= NUM; i++)
if (prime[i] == 1)
primefinal[idxz++] = i;
printf("\n");
int idx2 = 0;
int idx = 0;
int wtf = 82025;
printf("Start calculating.. \n");
do {
idx2 = idx;
do {
int mapidx = primefinal[idx2] + primefinal[idx];
if (mapidx > 0x100000 * 4) {
printf("assert..%x %x %x %x %x", mapidx, primefinal[idx2], primefinal[idx], idx2, idx);
return 0;
}
finaldata[mapidx]++;
1 + 1;
idx += 1;
1 + 1;
} while (idx != wtf);
idx = idx2 + 1;
} while (idx2 + 1 != wtf);
// Getting a flag string
int asd[] = { 1500, 2160, 2178, 2412, 2454, 3880, 4930, 5138, 12360, 15378, 15972, 16734, 17808, 18126, 19524, 19728, 21700, 22026, 23660, 27480, 27550, 27692, 28830, 29830, 30640, 31066, 31720, 32960, 33286, 34480, 35392, 35714, 35994, 36160, 36312, 37380, 37622, 38214, 39324, 39414, 40504, 40528, 40894, 40914, 41044, 41322, 41626, 41804, 41854, 41860, 42018, 42238, 42342, 42586, 42724, 43148, 43168, 43214, 43442, 0 };
int arrSize = sizeof(asd) / sizeof(asd[0]);
for (int z = 0; z < arrSize; z++) {
printf("%c", finaldata[asd[z]]);
}
return 0;
}
So, Flag is CODEGATE2020{JMP!_JNE!_JE!_R4bB1t_Kn0w_G01dB4cH_C0njeCTuRe}.